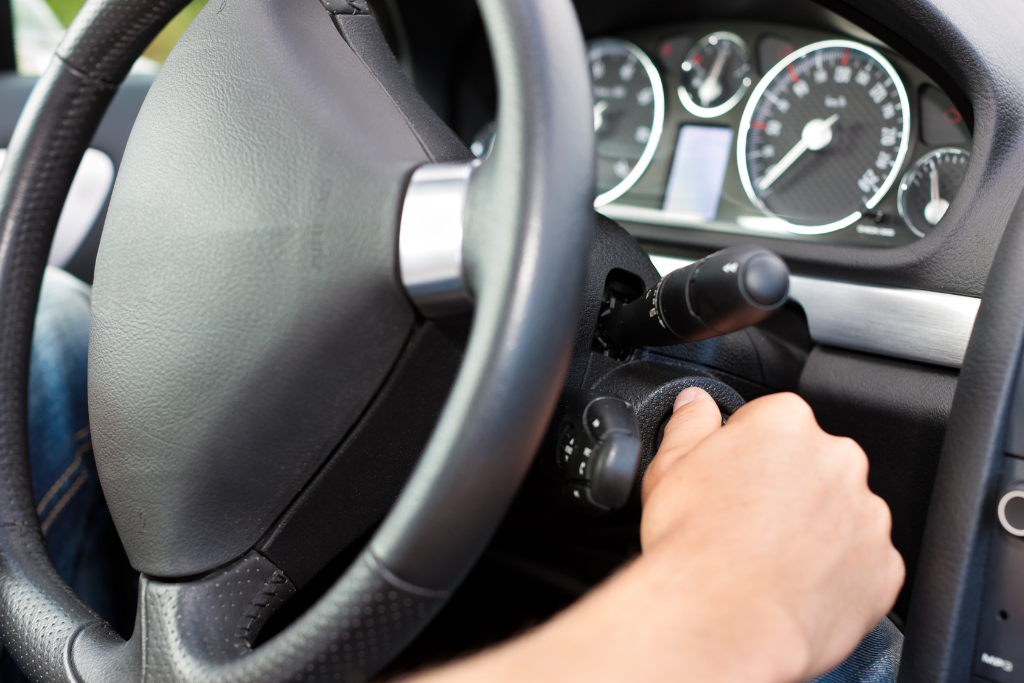
How to Start an Automatic Car with a Key: is a fundamental skill every driver must master. Whether you’re a new driver or transitioning from a manual transmission vehicle, understanding the precise steps for starting an automatic car key ensures a smooth and safe driving experience. This guide will walk you through every aspect of initiating your vehicle’s operation with confidence and precision.

Understanding Automatic Car Key Systems
Types of Key Systems
- Traditional Metal Key
- Key Fob with Push-Button Start
- Smart Key with Proximity Activation
- Electronic Transponder Keys
Modern Key Technologies
- Advanced security features
- Electronic communication
- Encrypted vehicle access
- Anti-theft protection mechanisms
Prerequisite Checks Before Starting
Vehicle Preparation
- Ensure parking brake is engaged
- Shift gear to “Park” position
- Check dashboard warning lights
- Verify fuel level
- Confirm key battery functionality
Safety Considerations
- Adjust seat and mirrors
- Fasten seat belt
- Clear surrounding area
- Check instrument cluster
- Ensure no obstructions
Step-by-Step Starting Procedure
Traditional Key Method
- Insert key into ignition
- Fully insert without excessive force
- Rotate key smoothly to “Start” position
- Release key once engine starts
- Allow engine brief warm-up period
Modern Push-Button Start
- Ensure key fob inside vehicle
- Depress brake pedal completely
- Press engine start button
- Wait for engine initialization
- Release brake once engine running
Troubleshooting Starting Issues
Common Starting Challenges
- Weak battery
- Faulty key system
- Electrical interference
- Security system activation
- Mechanical ignition problems
Diagnostic Steps
- Check key battery
- Verify key programming
- Inspect ignition mechanism
- Test battery voltage
- Consult vehicle manual
Key Maintenance Strategies
Preventive Care
- Regular key battery replacement
- Avoid physical damage
- Keep key clean
- Store in moderate temperatures
- Use protective key cases
Professional Maintenance
- Annual key system inspection
- Electronic diagnostic checks
- Periodic security system evaluation
- Professional key programming
Advanced Starting Techniques
Cold Weather Considerations
- Allow extra warm-up time
- Use recommended engine oil
- Avoid extended idling
- Monitor battery performance
- Use block heater if available
High-Altitude Starting
- Adjust starting procedures
- Monitor engine performance
- Use appropriate fuel grades
- Consider engine modifications
- Follow manufacturer recommendations
Electronic Key Complexities
Signal Transmission
- Radio frequency communication
- Encrypted authentication
- Rolling code mechanisms
- Proximity detection
- Immobilizer integration
Security Protocols
- Unique vehicle identification
- Anti-theft protection
- Unauthorized access prevention
- Constant signal verification
- Advanced encryption technologies
Potential Starting Complications
Battery and Electrical Issues
- Weak vehicle battery
- Corroded battery terminals
- Alternator malfunction
- Electrical system disruptions
- Component wear and tear
Key System Failures
- Electronic component breakdown
- Signal transmission problems
- Transponder chip malfunction
- Programming inconsistencies
- Mechanical key wear
Best Practices
Recommended Habits
- Always carry spare key
- Understand your vehicle’s system
- Perform regular maintenance
- Stay informed about key technologies
- Follow manufacturer guidelines
Safety Recommendations
- Never leave running vehicle unattended
- Keep key away from electronic devices
- Avoid exposing key to extreme temperatures
- Use steering wheel lock
- Maintain comprehensive insurance
Technological Evolution
Future Key Technologies
- Biometric authentication
- Smartphone integration
- Advanced encryption
- AI-powered security systems
- Predictive maintenance features
Emerging Trends
- Keyless entry advancements
- Digital key platforms
- Enhanced vehicle connectivity
- Improved security protocols
- Seamless user experience
Causes of Car Key Starting Problems
Mechanical Causes
Key Issues
- Physical damage
- Worn key teeth
- Bent or deformed key
- Rust or corrosion
- Manufacturing defects
Ignition Cylinder Problems
- Mechanical wear
- Dust accumulation
- Internal component failure
- Misalignment
- Spring mechanism breakdown
Electrical Causes
Battery-Related Issues
- Weak car battery
- Dead battery
- Corroded battery terminals
- Electrical system drain
- Alternator malfunction
Electronic Key System Failures
- Transponder chip malfunction
- Key fob battery failure
- Signal transmission problems
- Electronic control unit (ECU) issues
- Wiring system disruptions
Security System Complications
Anti-Theft Mechanisms
- Security system lockout
- Incorrect key authentication
- Immobilizer activation
- Encrypted key communication failures
- System reset requirements
Vehicle-Specific Factors
Manufacturer Design
- Proprietary key technologies
- Complex electronic integration
- Sensitivity to environmental conditions
- Unique security protocols
- Manufacturing tolerances
Vehicle Age
- Component degradation
- Technological obsolescence
- Cumulative system stress
- Increased mechanical wear
- Electronic system limitations
Environmental Influences
Temperature Effects
- Extreme heat damage
- Cold weather battery performance
- Mechanical contraction/expansion
- Electronic component sensitivity
- Lubrication system challenges
Exposure Conditions
- Moisture infiltration
- Salt and chemical exposure
- Dust and debris accumulation
- UV radiation damage
- Mechanical stress
User-Related Causes
Handling Problems
- Improper key usage
- Physical damage
- Incorrect storage
- Exposure to harsh conditions
- Repeated mechanical stress
Maintenance Neglect
- Lack of key system checks
- Irregular battery maintenance
- Delayed component replacement
- Inadequate cleaning
- Missed professional diagnostics
Technological Complexities
Signal Interference
- Electronic device proximity
- Radio frequency disruptions
- Electromagnetic interference
- Communication protocol conflicts
- Encryption system challenges
Software Limitations
- Outdated vehicle software
- Firmware compatibility issues
- Programming inconsistencies
- Communication protocol errors
- System configuration conflicts
Factors Affecting Car Key Starting
Technological Factors
Key System Design
- Electronic transmission protocols
- Encryption mechanisms
- Signal frequency
- Authentication complexity
- Transponder chip technology
Communication Systems
- Radio frequency capabilities
- Electronic control unit integration
- Security system interactions
- Signal transmission reliability
- Proximity detection accuracy
Vehicle-Specific Factors
Manufacturer Engineering
- Electronic system complexity
- Security protocol design
- Manufacturing precision
- Computer system integration
- Key recognition algorithms
Vehicle Age Impact
- Electronic component degradation
- Software compatibility
- System update limitations
- Technological obsolescence
- Mechanical wear progression
Electrical Considerations
Power System Dynamics
- Battery voltage stability
- Electrical system integrity
- Current transmission efficiency
- Alternator performance
- Wiring system condition
Electronic Component Reliability
- Key fob battery strength
- Signal processing capabilities
- Electronic circuit durability
- Component interconnectivity
- Resistance to environmental stress
Mechanical Influences
Physical Key Characteristics
- Material composition
- Precision of key cutting
- Mechanical wear resistance
- Surface integrity
- Dimensional accuracy
Ignition Mechanism
- Cylinder alignment
- Mechanical tolerance
- Lubrication effectiveness
- Component wear patterns
- Precision of mechanical interfaces
Environmental Factors
Temperature Impacts
- Electronic component performance
- Battery chemical reactions
- Material expansion/contraction
- Signal transmission reliability
- Mechanical system responsiveness
Exposure Conditions
- Humidity effects
- Dust and debris interference
- Corrosive environment challenges
- Electromagnetic interference
- Mechanical stress exposure
Security System Parameters
Authentication Mechanisms
- Encryption complexity
- Rolling code technologies
- Unique identification protocols
- Signal verification processes
- Immobilizer system integration
Anti-Theft Technologies
- Signal scrambling techniques
- Proximity detection accuracy
- Electronic fingerprinting
- Unauthorized access prevention
- Real-time authentication
Maintenance Considerations
System Performance
- Regular diagnostic checks
- Key system calibration
- Electronic component maintenance
- Software update frequency
- Preventive maintenance strategies
Operational Consistency
- Signal transmission reliability
- Electronic system responsiveness
- Mechanical precision
- Component interoperability
- Long-term system stability
User Interaction Factors
Operational Expertise
- Understanding key system
- Proper handling techniques
- Maintenance awareness
- Technological adaptation
- System-specific knowledge
Usage Patterns
- Frequency of use
- Storage conditions
- Handling care
- Environmental exposure
- Maintenance regularity
Car Key Starting Causes:
Mechanical Failures
- Worn key teeth
- Damaged ignition cylinder
- Physical key deformation
- Mechanical component wear
- Misaligned key mechanisms
Electrical Problems
- Dead car battery
- Corroded battery terminals
- Faulty transponder chip
- Electrical system interruptions
- Weak key fob battery
- ECU (Electronic Control Unit) malfunction
Security System Complications
- Triggered anti-theft system
- Authentication failures
- Immobilizer activation
- Encryption communication errors
- Incorrect key recognition
Electronic Interference
- Radio frequency disruptions
- Signal transmission failures
- Electromagnetic interference
- Communication protocol conflicts
- Proximity sensor malfunction
Environmental Factors
- Extreme temperature impacts
- Moisture damage
- Dust and debris accumulation
- Corrosive environment exposure
- Material degradation
User-Related Causes
- Improper key handling
- Lack of maintenance
- Irregular key usage
- Physical key damage
- Incorrect storage conditions
Vehicle-Specific Issues
- Aging electronic systems
- Manufacturer design limitations
- Software compatibility problems
- Technological obsolescence
- Complex key authentication protocols
Critical Diagnostic Considerations
- Comprehensive system evaluation
- Professional key system analysis
- Regular maintenance checks
- Understanding vehicle-specific technologies
- Proactive component replacement
Key starting problems result from complex interactions between mechanical, electrical, and technological systems, requiring systematic diagnostic approaches.
Benefits of Reliable Car Key Starting
Personal Convenience
- Immediate vehicle access
- Reduced starting anxiety
- Consistent transportation readiness
- Minimal operational disruptions
- Simplified vehicle interaction
Financial Advantages
- Prevent emergency service costs
- Reduce potential towing expenses
- Minimize unexpected repair bills
- Lower insurance claim risks
- Optimize vehicle maintenance
Safety Benefits
- Reliable emergency transportation
- Predictable vehicle performance
- Enhanced personal security
- Reduced roadside vulnerability
- Quick evacuation capabilities
Technological Advantages
- Advanced security features
- Sophisticated key authentication
- Seamless electronic integration
- Encryption protection
- Anti-theft mechanisms
Performance Optimization
- Consistent engine start
- Precise electronic communication
- Reduced mechanical stress
- Improved vehicle longevity
- Efficient energy transmission
Psychological Benefits
- Peace of mind
- Confidence in vehicle reliability
- Reduced transportation stress
- Enhanced driving experience
- Sense of control
Maintenance Benefits
- Early problem detection
- Proactive system monitoring
- Comprehensive diagnostic insights
- Preventative maintenance opportunities
- Extended key system lifespan
Practical Advantages
- Multiple key configuration options
- Flexible access methods
- Support for various driving scenarios
- Adaptable to different environments
- User-friendly technological integration
Effective car key starting ensures reliable, secure, and efficient vehicle operation across diverse conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About How to Start an Automatic Car with a Key:
How do I start an automatic car?
- Insert key in ignition
- Ensure gear is in “Park”
- Depress brake pedal
- Rotate key or press start button
- Release key once engine starts
What if the key won’t turn?
Potential causes:
- Steering wheel locked
- Gear not fully in “Park”
- Dead battery
- Faulty ignition cylinder
- Key damage
Why won’t my key start the car?
Possible reasons:
- Weak car battery
- Damaged key
- Faulty transponder
- Security system activation
- Electrical system failure
How do I unlock a stuck steering wheel?
- Gently turn steering wheel
- Apply slight pressure
- Simultaneously turn key
- Avoid excessive force
- Check for mechanical issues
Do all automatic cars start the same way?
Variations include:
- Traditional key insertion
- Push-button start
- Smart key proximity systems
- Manufacturer-specific protocols
How long should I hold the key when starting?
- 2-3 seconds maximum
- Release immediately after engine starts
- Avoid extended cranking
- Modern cars require minimal holding time
How often should I replace my car key?
Replace when:
- Physical damage occurs
- Electronic functions fail
- Battery consistently weak
- Key shows significant wear
- Every 5-7 years
What causes key starting failures?
Common issues:
- Battery problems
- Electrical system failures
- Key chip malfunction
- Ignition cylinder wear
- Security system conflicts
Can I start the car in neutral?
Recommended practices:
- Always start in “Park”
- Some vehicles allow “Neutral”
- Consult vehicle manual
- Follow manufacturer guidelines
What if the key doesn’t turn?
Troubleshooting steps:
- Check gear position
- Verify battery charge
- Gently wiggle steering wheel
- Inspect key for damage
- Try spare key
How do push-button starts work?
Key requirements:
- Key fob inside vehicle
- Brake pedal depressed
- Electronic authentication
- Proximity sensor activation
- Security code verification
Are smart keys more secure?
Advantages include:
- Advanced encryption
- Rolling code technology
- Proximity detection
- Reduced theft risk
- Complex authentication
What if my key breaks?
Immediate actions:
- Contact dealership
- Use spare key
- Professional key extraction
- Consider key replacement
- Avoid DIY repairs
How to start with a dead key fob battery?
Emergency methods:
- Use physical key inside fob
- Place fob near start button
- Replace key fob battery
- Use dealer’s backup method
- Consult vehicle manual
Conclusion
Starting an automatic car requires understanding both mechanical procedures and electronic complexities. By mastering these techniques, drivers can ensure reliable, secure, and efficient vehicle operation across various conditions and technological platforms.